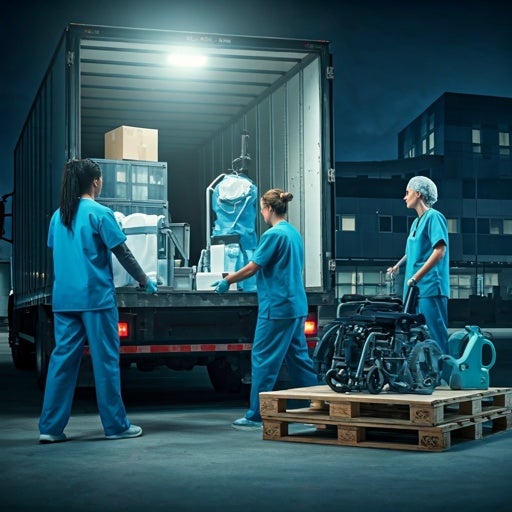

The centralization of medical device processing to one facility is becoming more prevalent. Centralizing sterile processing activities reduces expenses while concentrating expertise. However, this also introduces new concerns. When sterile processing is located within the same building where instrumentation is used, transport occurs over smooth floors in a controlled environment…
Editor’s Note: This page is a companion piece to the main article, Centralized sterile processing cuts costs, complexity for four ASCs. Implementing offsite sterilization is a major project. At Total Joint Specialists, our journey began gradually, growing in scope over time as the team became comfortable with the process…

Editor's Note New and revised sterilization and reprocessing standards are reshaping the landscape for sterile processing departments, placing greater emphasis on chemical modalities, device-specific protocols, and system-wide quality management, according to the Healthcare Purchasing News May 27 update on compliance and standards. Among the most significant developments is the overhaul…

Preventing infection from contaminated surgical tools requires attention to every link in a complex chain of processes, from point-of-use pretreatment in the OR to the moment the freshly disinfected or sterilized item arrives at the next patient’s bedside. For those on the front lines, manufacturers’ written instructions for use (IFUs)…

In the OR, precision and focus can mean the difference between life and death. However, surgical patient outcomes hinge on more than the competence of those working in these inherently intense environments. Every procedure also depends on the laborious, behind-the-scenes efforts of the people responsible for ensuring every surgical instrument…
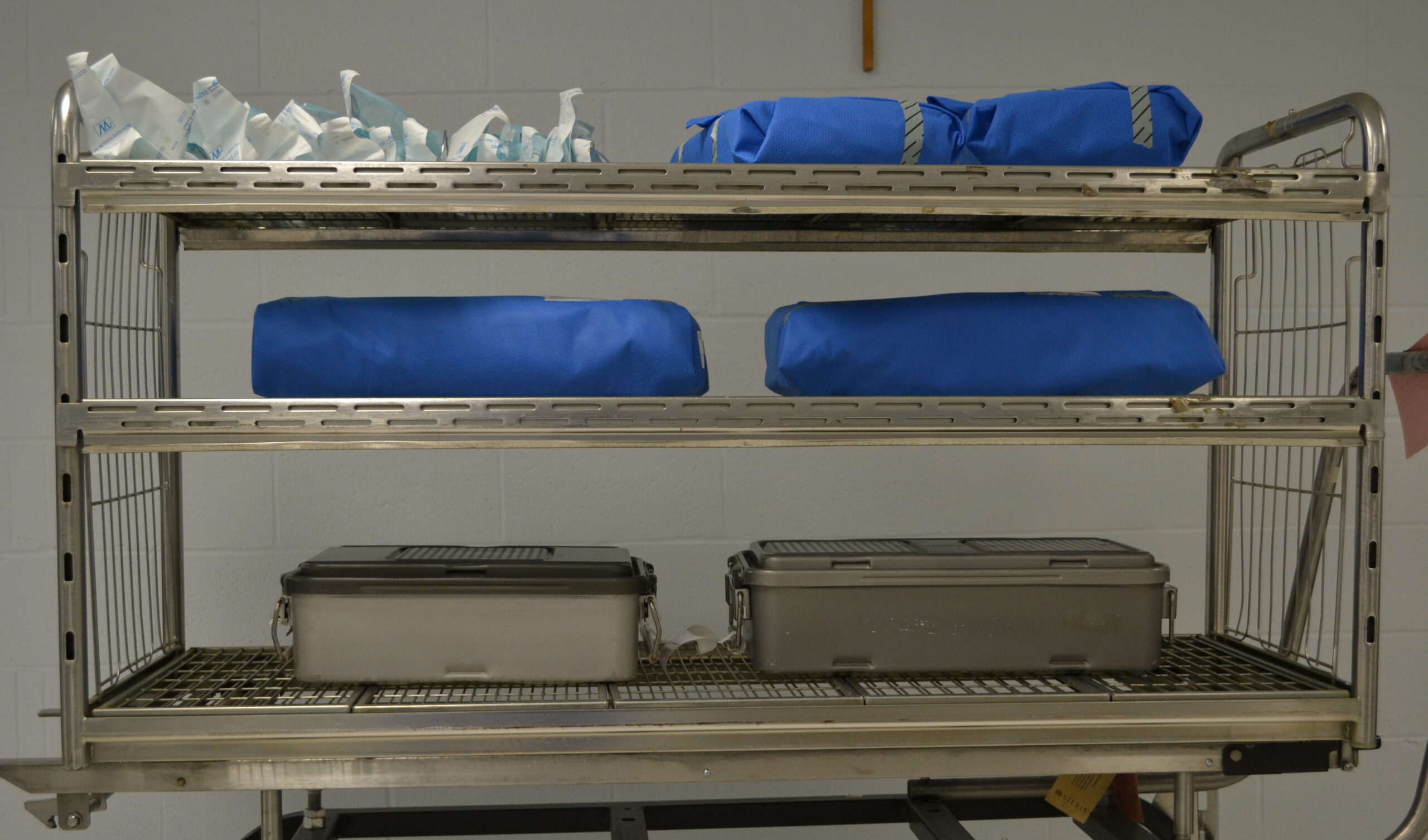

Reliable and robust enough for daily use on most medical devices, steam is the most common sterilant in healthcare facilities. However, using steam properly requires a balancing act. For example, too much moisture can lead to wet packs, while steam that is too dry might not be sufficient to achieve…

Editor's Note New guidance from The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) addresses regulatory and safety concerns for hospitals using ethylene oxide (EO) for medical device sterilization—a pressing concern due to EO’s effectiveness but associated health risks. ANSI/AAMI ST58:2024, an update on chemical sterilization and high-level disinfection practices…

Editor's Note In a new guidance document for manufacturers of pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals, The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) has released a new guidance document updating best practices for radiation sterilization validation and routine control of single-use systems. The document, AAMI CR513:2024; Guidance on radiation sterilization validation and…
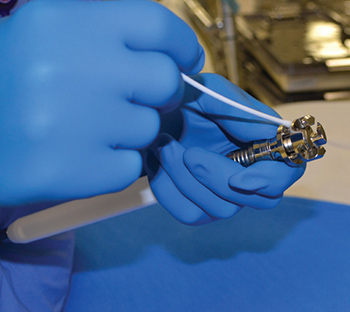
Inspecting surgical devices is a time-consuming process. However, diligently checking every instrument prior to sterilization is essential to ensuring safe, proper functioning. As the last people to see devices before they are used for patient care, sterile processing technicians must be thorough. Exterior surfaces should be inspected for flaws such…

Editor's Note A new guidance document covering the entire process for the selection, labeling, and sterile processing of dilators and ultrasound probes is available from The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI). Released April 17, AAMI TIR99:2024; Processing Of Dilators, Transesophageal And Ultrasound Probes In Health Care Facilities…